Highlighter
The xMap library provides powerful code highlighting capabilities that bring your TypeScript code snippets to life with semantic syntax highlighting. This document covers the highlighter component, focusing on highlightCode the function and underlying mechanisms.
Imports
You can import the ANSI component in two ways:
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';highlightCode
The highlightCode function is the main entry point for syntax highlighting in xMap.
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
const code = `
function greet(name: string): string {
return 'Hello, ' + name;
}
`;
const highlightedCode = highlightCode(code);
console.log(highlightedCode);The function returns the same code string but with ANSI color codes inserted to highlight different syntax elements.
Custom Color Schemes
You can customize the highlighting by providing a partial color scheme:
import { xterm } from '@remotex-labs/xansi/xterm.component';
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
const code = `
function greet(name: string): string {
return 'Hello, ' + name;
}
`;
const customScheme = {
keywordColor: xterm.blue.bold,
stringColor: xterm.green,
functionColor: xterm.yellow
};
const highlightedCode = highlightCode(code, customScheme);
console.log(highlightedCode);Output: 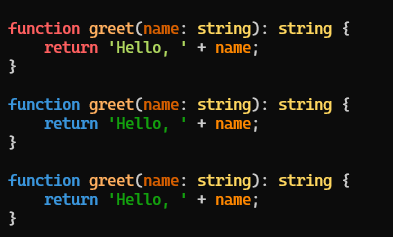
How the Highlighter Works
The highlighter works by:
- Parsing the TypeScript code into an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)
- Walking through the AST nodes
- Identifying different code elements based on their syntax kind
- Applying appropriate colors based on the highlighting scheme
- Generating a new string with the ANSI color codes inserted
This approach provides accurate, semantic-based highlighting that understands the actual structure of your code.
Default Color Scheme
The default color scheme highlights different code elements with distinct colors:
| Element | Description | Default Color |
|---|---|---|
| Keywords | Reserved words like function, const, return | Light coral |
| Types | Type annotations and references | Light goldenrod yellow |
| Classes | Class declarations and references | Light orange |
| Interfaces | Interface declarations | Light goldenrod yellow |
| Strings | String literals | Olive green |
| Numbers | Numeric literals | Light gray |
| Functions | Function and method declarations | Light orange |
| Variables | Variable declarations and references | Burnt orange |
| Parameters | Function parameters | Deep orange |
| Comments | Code comments | Dark gray |
| Regular Expressions | Regex literals | Olive green |
| Properties | Object property access | Light yellow |
Custom Highlighting Examples
Example 1: Minimal Theme
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
const code = `
function greet(name: string): string {
return 'Hello, ' + name; // comment
}
`;
const minimalTheme = {
keywordColor: (text: string): string => `\x1b[1m${ text }\x1b[0m`, // Bold
stringColor: (text: string): string => `\x1b[3m${ text }\x1b[0m`, // Bold
commentColor: (text: string) :string => `\x1b[2m${ text }\x1b[0m` // Bold
};
const highlighted = highlightCode(code, minimalTheme);
console.log(highlighted);Example 2: High Contrast Theme
const highContrastTheme = {
keywordColor: (text: string): string => `\x1b[97;45m${ text }\x1b[0m`, // White on purple
functionColor: (text: string): string => `\x1b[97;44m${ text }\x1b[0m`, // Black on green
stringColor: (text: string): string => `\x1b[30;42m${ text }\x1b[0m`, // Bold
numberColor: (text: string) :string => `\x1b[97;41m${ text }\x1b[0m` // Bold
};
const highlighted = highlightCode(code, highContrastTheme);
console.log(highlighted);Example 3: Using xterm Colors
const colorfulTheme = {
keywordColor: xterm.magentaBright,
typeColor: xterm.cyanBright,
stringColor: xterm.greenBright,
functionColor: xterm.blueBright,
commentColor: xterm.gray
};
const highlighted = highlightCode(code, colorfulTheme);
console.log(highlighted)Integration with Other xMap Features
The highlightCode function works seamlessly with other xMap features: With formatCode:
import { formatCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
const code = `
function sum(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
`;
// First highlight, then format
const highlightedCode = highlightCode(code);
const formattedCode = formatCode(highlightedCode, {
padding: 5,
startLine: 0
});
console.log(formattedCode);With formatErrorCode:
import { formatErrorCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
const code = `
function divide(a: number, b: number): number {
if (b === 0) {
throw new Error('Division by zero');
}
return a / b;
}
`;
const sourcePosition = {
code: highlightCode(code), // Highlight first
line: 2,
column: 13,
startLine: 0,
endLine: 0,
name: null,
source: '',
sourceRoot: null,
sourceIndex: 0,
generatedLine: 0,
generatedColumn: 0
};
const formattedError = foWith SourceService:
import { formatErrorCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
// Assuming sourceService is initialized with a source map
const errorPosition = sourceService.getPositionWithCode(2, 3130, 1);
if (errorPosition) {
// Highlight the source code before formatting
errorPosition.code = highlightCode(errorPosition.code);
const formattedError = formatErrorCode(errorPosition);
console.log(formattedError);
}Advanced Usage
For more advanced use cases, you can directly use the CodeHighlighter class:
import ts from 'typescript';
import { xterm } from '@remotex-labs/xansi/xterm.component';
import { CodeHighlighter } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
const code = `
function example() {
return "Hello world";
}
`;
// Create a TypeScript source file
const sourceFile = ts.createSourceFile(
'example.ts',
code,
ts.ScriptTarget.Latest,
true
);
// Create custom scheme
const customScheme = {
enumColor: xterm.burntOrange,
typeColor: xterm.lightGoldenrodYellow,
classColor: xterm.lightOrange,
stringColor: xterm.oliveGreen,
keywordColor: xterm.lightCoral,
commentColor: xterm.darkGray,
functionColor: xterm.lightOrange,
variableColor: xterm.burntOrange,
interfaceColor: xterm.lightGoldenrodYellow,
parameterColor: xterm.deepOrange,
getAccessorColor: xterm.lightYellow,
numericLiteralColor: xterm.lightGray,
methodSignatureColor: xterm.burntOrange,
regularExpressionColor: xterm.oliveGreen,
propertyAssignmentColor: xterm.canaryYellow,
propertyAccessExpressionColor: xterm.lightYellow,
expressionWithTypeArgumentsColor: xterm.lightOrange
};
// Create highlighter instance
const highlighter = new CodeHighlighter(sourceFile, code, customScheme);
// Process the source file
function walkNodes(node: ts.Node): void {
highlighter.parseNode(node);
ts.forEachChild(node, walkNodes);
}
walkNodes(sourceFile);
// Get the highlighted code
const highlightedCode = highlighter.highlight();
console.log(highlightedCode);