Formatter
The xMap library provides powerful code formatting utilities that make it easier to display code snippets with line numbers, custom highlighting, and error indicators. This document covers two main formatting functions: formatCode and formatErrorCode.
Imports
You can import the ANSI component in two ways:
import { formatCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';formatCode
The formatCode function formats source code snippets with line numbers and optional custom formatting for specific lines. This is particularly useful for displaying code in documentation, error messages, or debugging output.
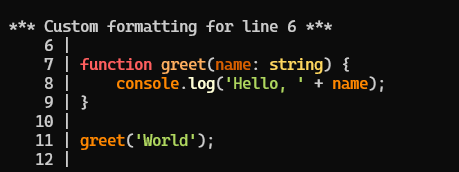
Basic Usage
import { formatCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
const code = `function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}`;
const formatted = formatCode(code);
console.log(formatted);Output:
1 | function sum(a, b) {
2 | return a + b;
3 | }Configuration Options
The formatCode function accepts an options object with the following properties:
| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
padding | number | 10 | The amount of padding for line numbers |
startLine | number | 0 | The starting line number (0-based) |
action | object | undefined | Custom action for specific lines |
Custom Line Actions
You can apply custom formatting to specific lines using the option: action
formatCode(code, {
padding: 8,
startLine: 5,
action: {
triggerLine: 7,
callback: (lineString, padding, lineNumber) => {
// Custom formatting logic
return lineString.replace(' ', ' > ');
}
}
});The callback function receives:
lineString: The formatted line string with padding and line numberpadding: The current padding valuelineNumber: The current line number
Examples
Basic formatting with custom padding:
import { formatCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
const code = `
function greet(name) {
console.log('Hello, ' + name);
}
greet('World');
`;
const formatted = formatCode(code, {
padding: 5,
startLine: 0
});
console.log(formatted);Output:
1 |
2 | function greet(name) {
3 | console.log('Hello, ' + name);
4 | }
5 |
6 | greet('World');Adding custom line formatting:
import { formatCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
const code = `
function greet(name) {
console.log('Hello, ' + name);
}
greet('World');
`;
const formatted = formatCode(code, {
padding: 8,
startLine: 0,
action: {
triggerLine: 3,
callback: (lineString, padding, lineNumber) => {
return `*** IMPORTANT CODE ON LINE ${ lineNumber } ***\n${ lineString }`;
}
}
});
console.log(formatted);Output:
1 |
2 | function greet(name) {
*** IMPORTANT CODE ON LINE 3 ***
3 | console.log('Hello, ' + name);
4 | }
5 |
6 | greet('World');
7 |formatErrorCode
The formatErrorCode function is specialized for highlighting errors in code snippets. It formats the code and adds a visual indicator (caret symbol ^) pointing to the exact error location.
Basic Usage
import { formatErrorCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
const sourcePosition = {
code: 'const x = 1;\nconst y = x.undefined;\n',
line: 2,
column: 13,
startLine: 0,
endLine: 0,
name: null,
source: '',
sourceRoot: null,
sourceIndex: 0,
generatedLine: 0,
generatedColumn: 0
};
const formatted = formatErrorCode(sourcePosition);
console.log(formatted);Output:
1 | const x = 1;
> 2 | const y = x.undefined;
| ^
3 |Customizing Error Indicators
You can customize the appearance of error indicators using ANSI color codes:
const ansiOption = {
color: (text) => `\x1b[31m${text}\x1b[0m` // Red color
};
const formatted = formatErrorCode(sourcePosition, ansiOption);The object allows: ansiOption
color: Function that applies color to the error indicatorreset: String to reset formatting (optional)
TIP
🎉 You can use xterm.red as color @see xAnsi
Examples
Basic error highlighting:
import { formatErrorCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
const sourcePosition = {
code: `function divide(a, b) {
if (b === 0) {
throw new Error('Division by zero');
}
return a / b;
}`,
line: 2,
column: 13,
startLine: 0,
endLine: 0,
name: null,
source: '',
sourceRoot: null,
sourceIndex: 0,
generatedLine: 0,
generatedColumn: 0
};
const formatted = formatErrorCode(sourcePosition);
console.log(formatted);Output:
1 | function divide(a, b) {
> 2 | if (b === 0) {
| ^
3 | throw new Error('Division by zero');
4 | }
5 | return a / b;
6 | }With custom ANSI colors:
import { xterm } from '@remotex-labs/xansi/xterm.component';
import { formatErrorCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
const sourcePosition = {
code: `function divide(a, b) {
if (b === 0) {
throw new Error('Division by zero');
}
return a / b;
}`,
line: 2,
column: 13,
startLine: 0,
endLine: 0,
name: null,
source: '',
sourceRoot: null,
sourceIndex: 0,
generatedLine: 0,
generatedColumn: 0
};
const ansiOption = {
color: xterm.red.bold.dim
};
const formatted = formatErrorCode(sourcePosition, ansiOption);
console.log(formatted);Combining with Other xMap Features
The formatting functions work particularly well when combined with other xMap features: With syntax highlighting:
import { formatCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
const code = `
function greet(name: string) {
return 'Hello, ' + name;
}
`;
// First highlight the code, then format it
const highlightedCode = highlightCode(code);
const formatted = formatCode(highlightedCode, {
padding: 5
});
console.log(formatted);With source maps and error reporting:
import { SourceService } from '@remotex-labs/xmap';
import { formatErrorCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/formatter.component';
import { highlightCode } from '@remotex-labs/xmap/highlighter.component';
// Create a SourceService from your source map
const sourceService = new SourceService(sourceMapJSON);
// Get code position with context
const errorPosition = sourceService.getPositionWithCode(1, 91);
// Add syntax highlighting to the code
if (errorPosition) {
errorPosition.code = highlightCode(errorPosition.code);
// Format with error highlighting
const formattedError = formatErrorCode(errorPosition, {
color: text => `\x1b[38;5;160m${ text }\x1b[0m`
});
console.log(formattedError);
}