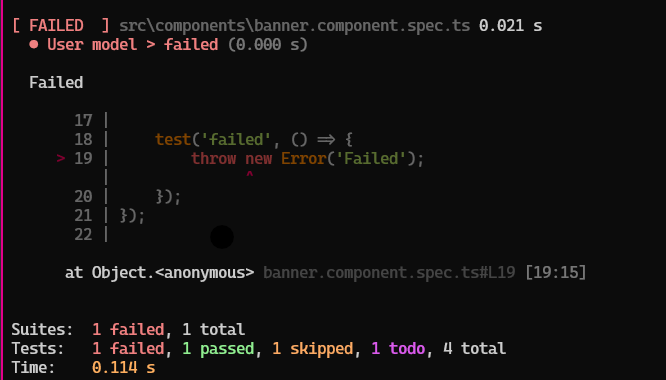
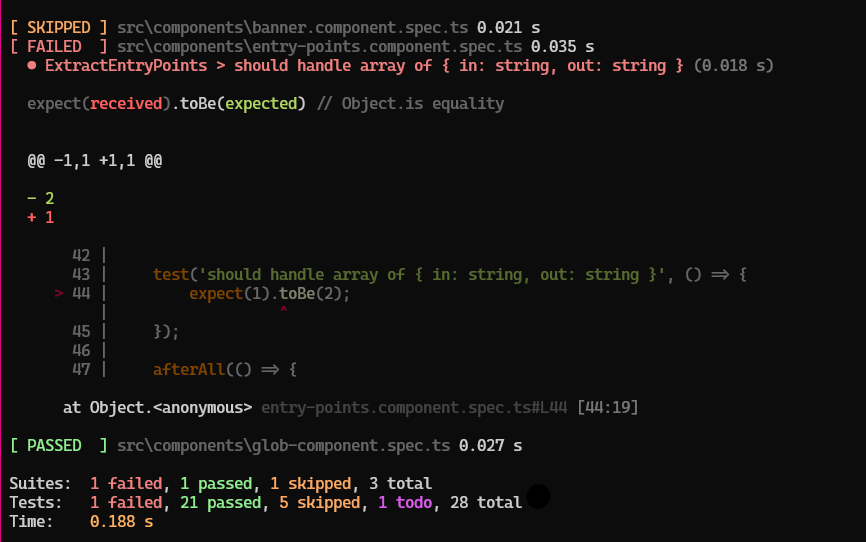
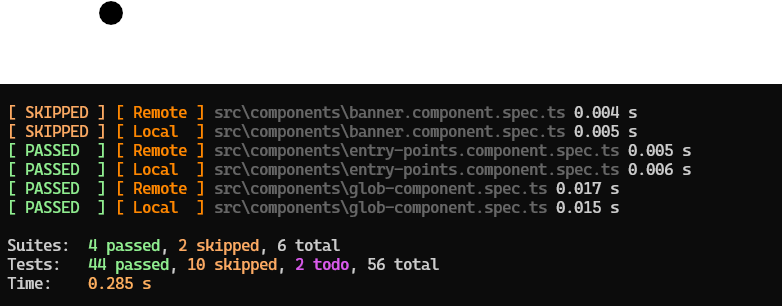
Guide
xJet is a modern, extensible test and mocking toolkit designed for JavaScript and TypeScript ecosystems. It combines test definitions, matchers, mocks, spies, logging utilities, and more, aiming to offer a streamlined, expressive, and highly productive developer experience for creating robust automated tests.
Key Features
Flexible Test Definitions:
Define tests using familiar patterns (test,it,describe, etc.), with support for lifecycle hooks (beforeEach,afterEach, etc.) and data-driven testing.Advanced Mocking:
Easily mock functions, constructors, and methods, including global and object-bound members, with features likemockImplementation,call history tracking, return value injection, and restoration of original implementations.
Powerful Spies:
Observe and assert upon function calls without altering their implementation.Comprehensive Matchers:
Rich set of matchers for all common data types, including objects, numbers, strings, and functions, designed for precise assertions and clear error messages.Integrated Logging:
Unified logging methods (log,info,warn,error,debug) routed to the test runner, enhancing test traceability and debugging.Automated Mock Management:
Easily clear, reset, or restore all mocks globally, ensuring stateful tests remain isolated and repeatable.TypeScript-Friendly:
All APIs are fully typed for maximum safety, autocomplete, and great IDE support.Runner Integration:
Outputs and logs are friendly for CI pipelines, terminals, and IDEs — helping you see what’s happening in tests at a glance.
Typical Usage Example
describe('User model', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
xJet.resetAllMocks();
});
test('creates a user with default status', () => {
const user = new User('Alice');
expect(user.status).toBe('active');
});
test('logs errors on invalid input', () => {
const logSpy = xJet.spyOn(console, 'error');
new User(null);
expect(logSpy).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
test('can be mocked', () => {
const constructorMock = xJet.mock(User);
constructorMock.mockImplementation((name) => ({ name: `Mocked ${ name }` }));
const user = new User('Bob');
expect(user.name).toBe('Mocked Bob');
constructorMock.mockRestore();
});
});Core Modules
Test Definition & Lifecycle:
describe,test,it,beforeAll,afterAll,beforeEach,afterEachMocking & Spying:
xJet.mock,xJet.fn,xJet.spyOnMatchers:
expect(...).toBe(...),.toEqual(...),.toHaveBeenCalled(), and moreLogging:
xJet.log,xJet.info,xJet.warn,xJet.error,xJet.debugGlobal Utilities:
Utilities for managing test and mock state, configuration, and reporting
Getting Started
- Add
@remotex-labs/xjetas a dependency to your project - Initialize your test files with
xJetglobals available - Use the provided APIs for defining, structuring, and verifying your tests with optimal productivity and clarity
Run: